43 label atp molecule
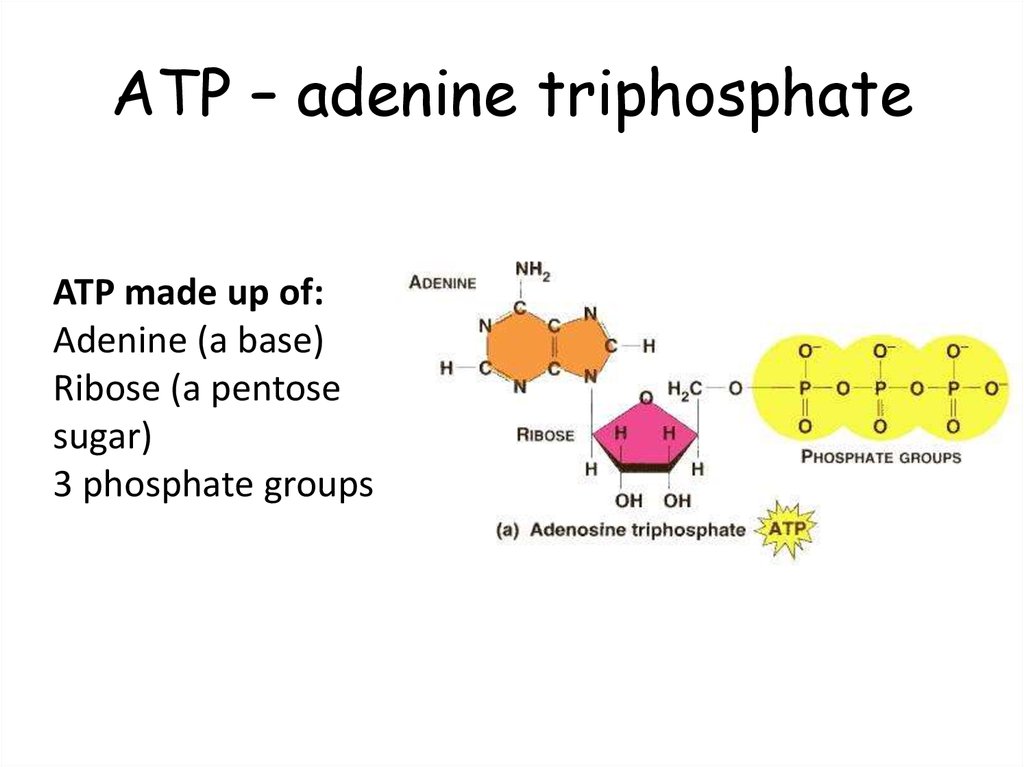
Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Adenosine triphosphate, commonly known as ATP, is the energy carrier molecule in living cells. ATP is structurally composed of Adenine molecule (a nitrogenous base), Ribose (pentose sugar) and three phosphate groups. Energy in ATP is stored in the bonds that hold the phosphate groups together. Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Answer: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram.
Label atp molecule
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc.Ribose PAdenine P Model of ATP Molecule | Perkins eLearning Preparation: Build an ATP Model First, build your five-carbon sugar, RIBOSE. Use five Popsicle sticks, and hot glue them into a pentagon. Then, hot glue cotton balls on each corner of the shape. Next, build the base, ADENINE. This is going to look like one pentagon and one hexagon stuck together on one side.
Label atp molecule. Unit 7.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure... 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure to include the 3 parts. 2. What is the process called when a phosphate is added to the ADP molecule a. Photosynthesis b. Phosphorylation c. Permeability d. Precipitation 3. The metabolism (breakdown) of ________________ in the mitochondria provides the energy for the phosphorylation of ADP. a. ATP b. Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is commonly referred to as the "energy currency" of the cell, as it provides readily releasable energy in the bond between the second and third phosphate groups. Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Summary of nucleic acid labeling methods. 1. 5′ end-labeled primers can be used with this method in order to add a 5′ modification to a DNA probe. 2. Modified nucleotides can be added to the 3′ recessed-end of double-stranded DNA during fill-in reactions. 3. SOLVED:Hand draw (pen, pencil, crayon, etc) and label the structure of ... Hand draw (pen, pencil, crayon, etc) and label the structure of a molecule of ATP (not a mitochondrium). Identify which specific part of the molecule produces the energy to facilitate metabolic processes, and how that happens, in your own words. It doesn't need to be highly technical. There is no partial credit.
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides T7 works well with UTP, CTP, and ATP but not with GTP. RNA 3' End labeling. T4 RNA ligase can be used to 3'-end label RNA molecules. The enzyme catalyzes the ligation of the 5' phosphate terminus of a radiolabeled nucleotide to the 3'-hydroxyl terminus of a single-stranded DNA or RNA oligo in an ATP-dependent manner. radioactive molecule used to label dna - OurChurchPress.com History of DNA - Scientists DRAFT. A common label is the small molecule biotin, Non radioactive labels often are more rapidly detected and are safer to use than radioisotopes. A small amount of DNA can be loaded into a … Here a new, labelled dNTP ([a 32-P]ATP or biotin-labelled dNTP) is added to the 3′-end of DNA by enzyme terminal ... Imaging Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - PMC INTRODUCTION. Significant efforts have been made over the decades to directly visualize adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in living systems. ATP is a molecule at the center of metabolism and signaling both inside and outside the living cell, and its universal importance in biology reaches well beyond its most familiar role as an energy metabolite.
ATP Diagram | Quizlet a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di. two. ATP Cycle. a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP. Phosphate Group (removed) a phosphate is removed to release energy. Phosphate Group (added) A phosphate group is added using a small amount of energy. atp molecule labeled - DaVinci Custom Linear Fireplaces [34] Mutations have been found throughout the ATRX protein, with over 90% of them being located in the zinc finger and helicase domains. They also play an important role in sensing viral RNAs. Label each part of the atp molecule above in the spaces provided. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. How does atp differ from adp. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases. ATP Molecule Structure: Fuel of Life - Indigo Instruments Conclusion. According to Sunyoung Kim, a biological chemist, he explains that "ATP is the fuel of life. It's an energy currency molecule — the most important source of chemical and mechanical energy in living systems". Therefore, ATP plays a vital role in the biological world. All living cells use Adenosine Triphosphate molecules as a ...
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 - PubChem ATP is an adenosine 5'-phosphate in which the 5'-phosphate is a triphosphate group. It is involved in the transportation of chemical energy during metabolic pathways. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a micronutrient, a fundamental metabolite and a cofactor. It is an adenosine 5'-phosphate and a purine ribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate.
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure and hydrolysis. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions.
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing | Chegg.com 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6.
atp molecule Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet every cell on earth used ATP to do work. ATP has energy that cells can directly use for cell processes. Active transport muscle movement chemical reactions. breaking the bond between the second and third phosphate group. Why is ATP considered the universal ene…. every cell on earth used ATP to do work.
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
ATP analogues at a glance - The Company of Biologists Recently, the EDA-ATP intermediate has been employed as a starting point for a number of fluorescent analogues that have been used to investigate motor proteins (Jameson and Eccleston, 1997; Bagshaw, 1998). In particular, derivatives such as Cy3-EDA-ATP can readily be detected at the single molecule level by laser microscopy (Oiwa et al., 2000 ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound and hydrotrope that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.



Post a Comment for "43 label atp molecule"