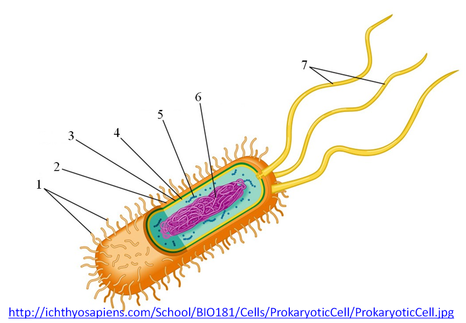
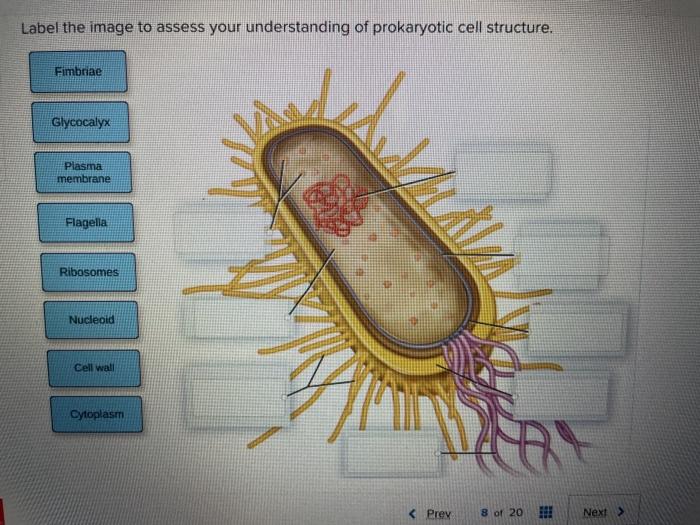
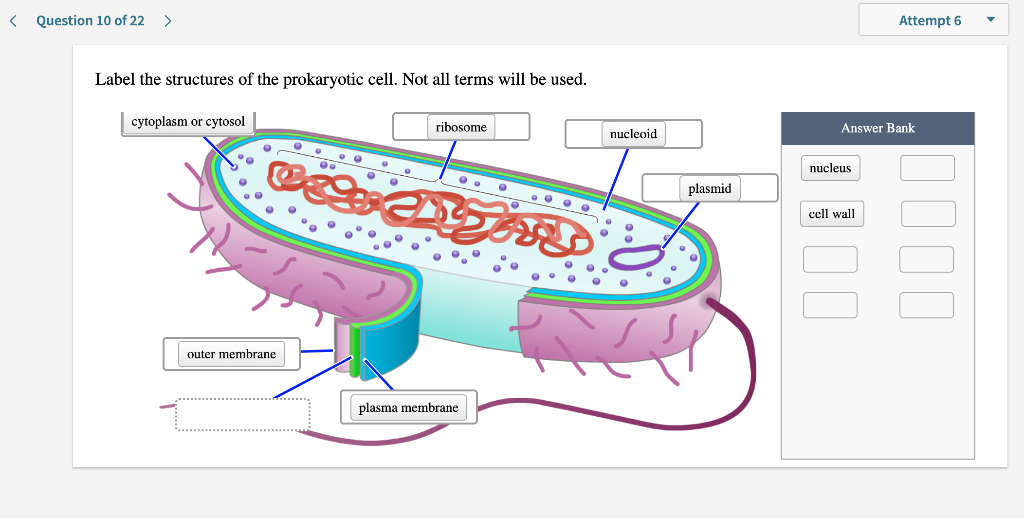
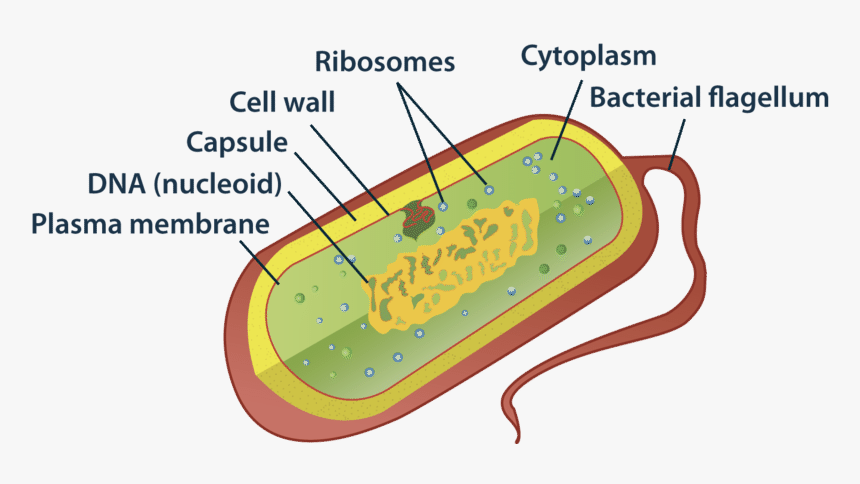
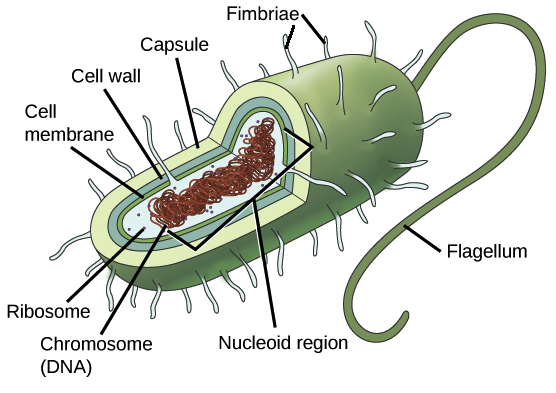
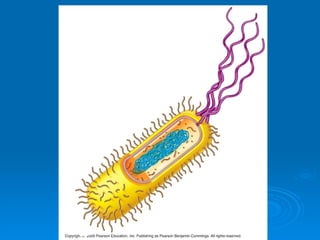
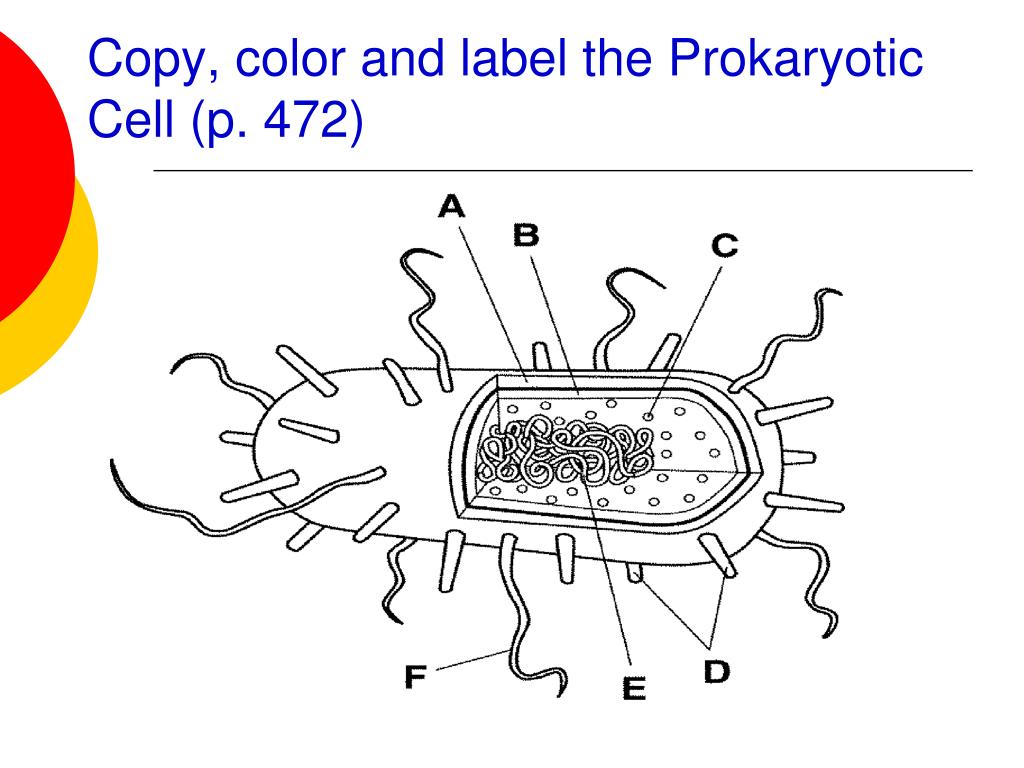
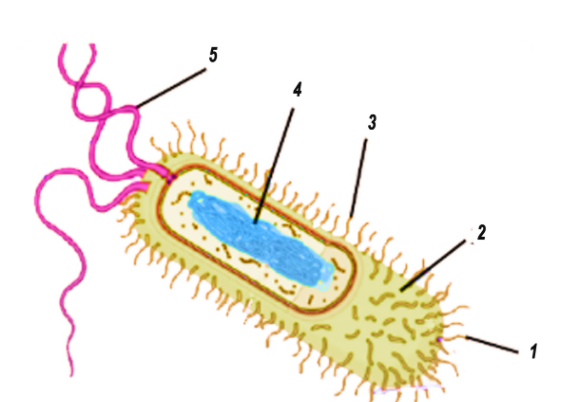
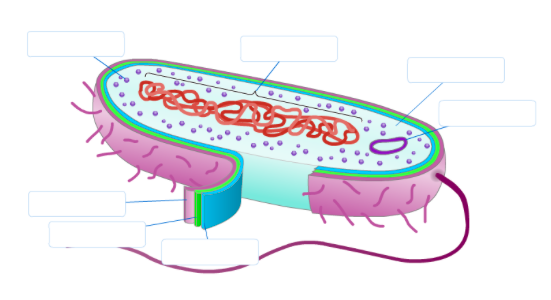
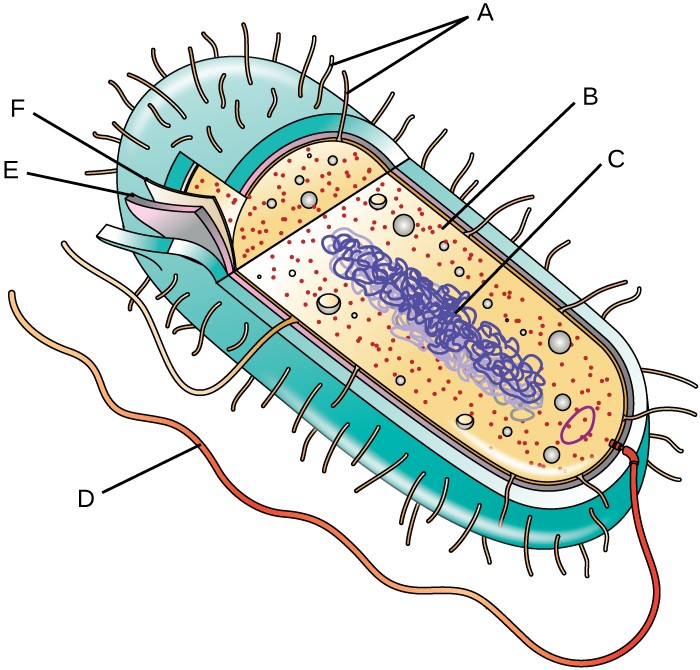
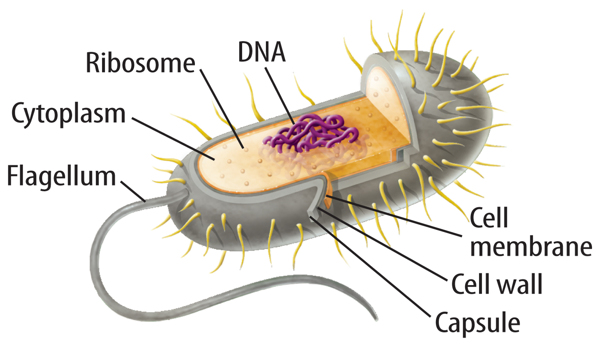
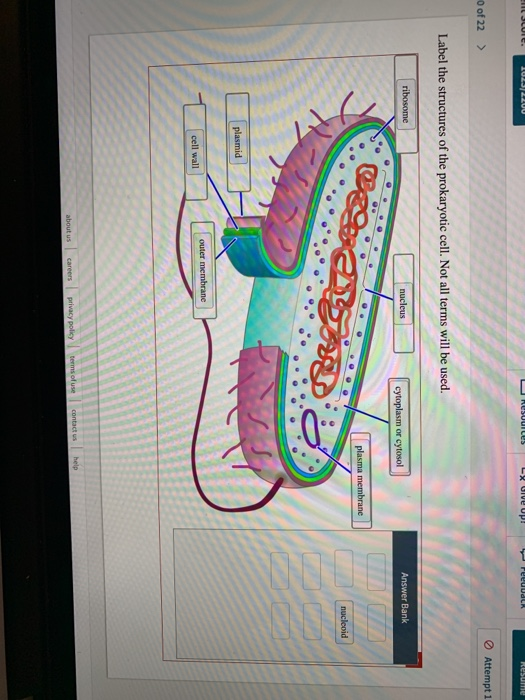
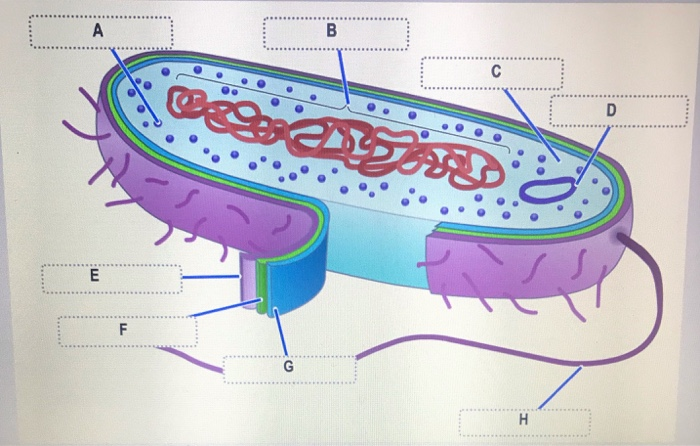
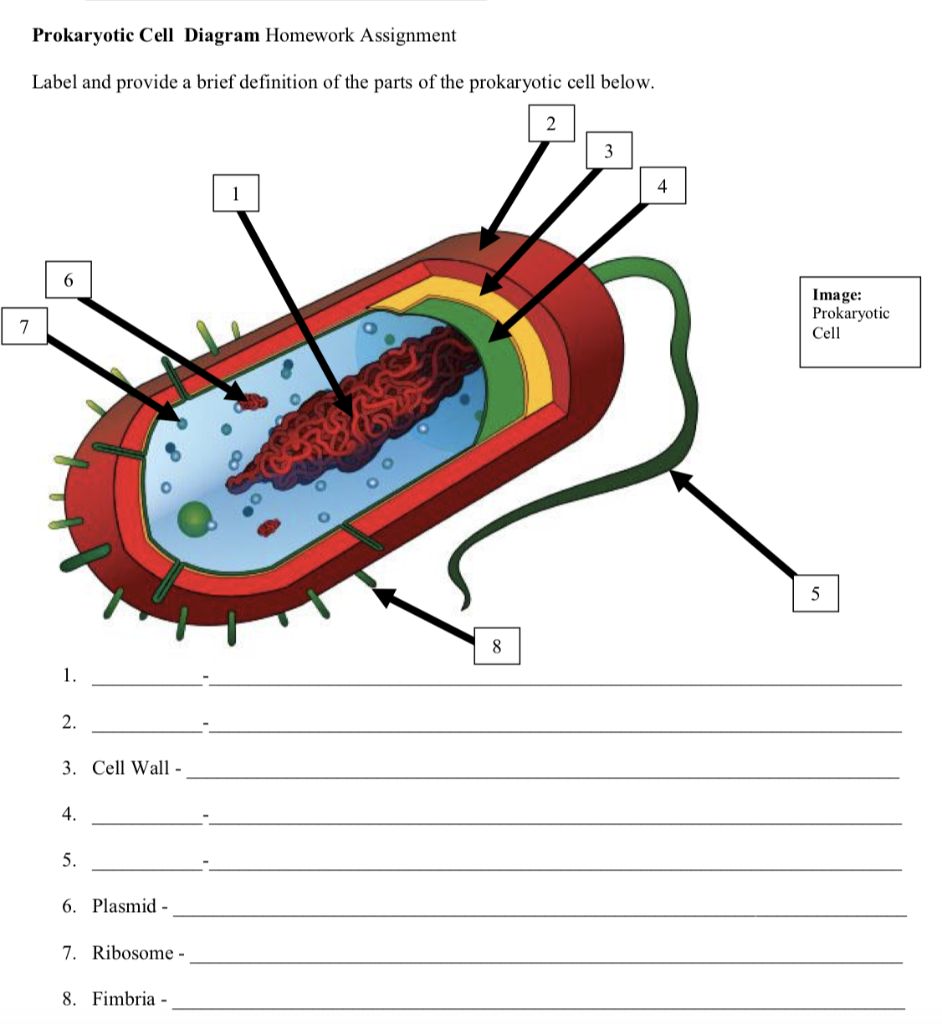
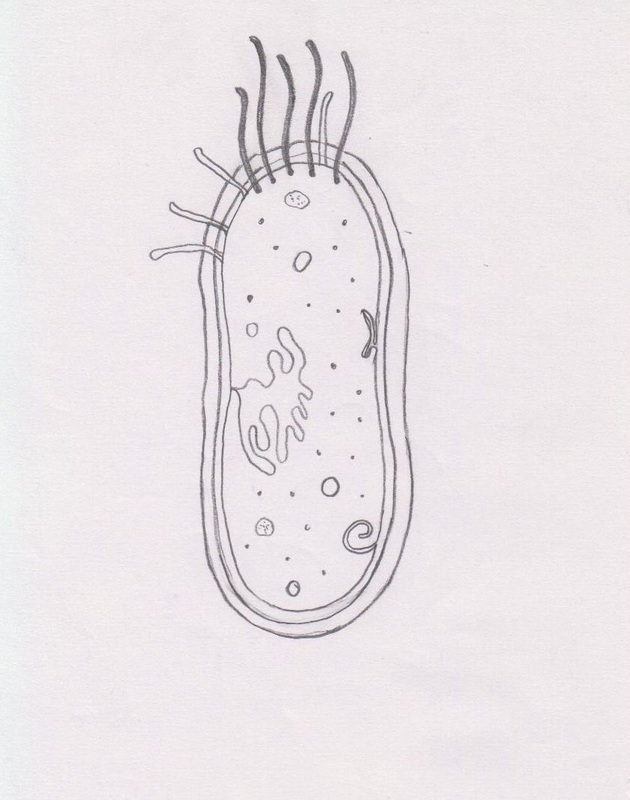
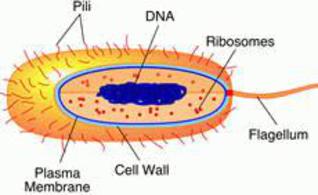
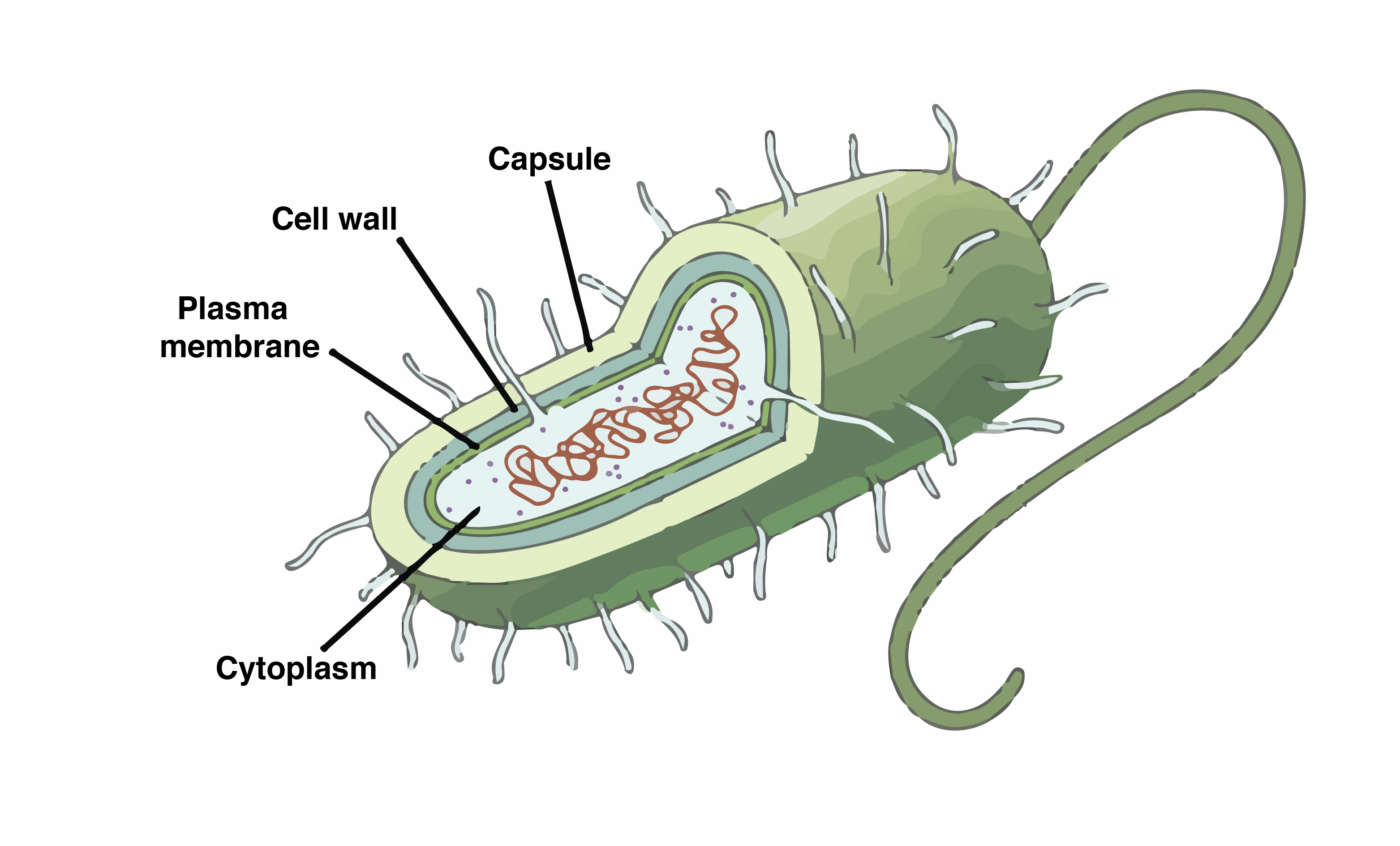
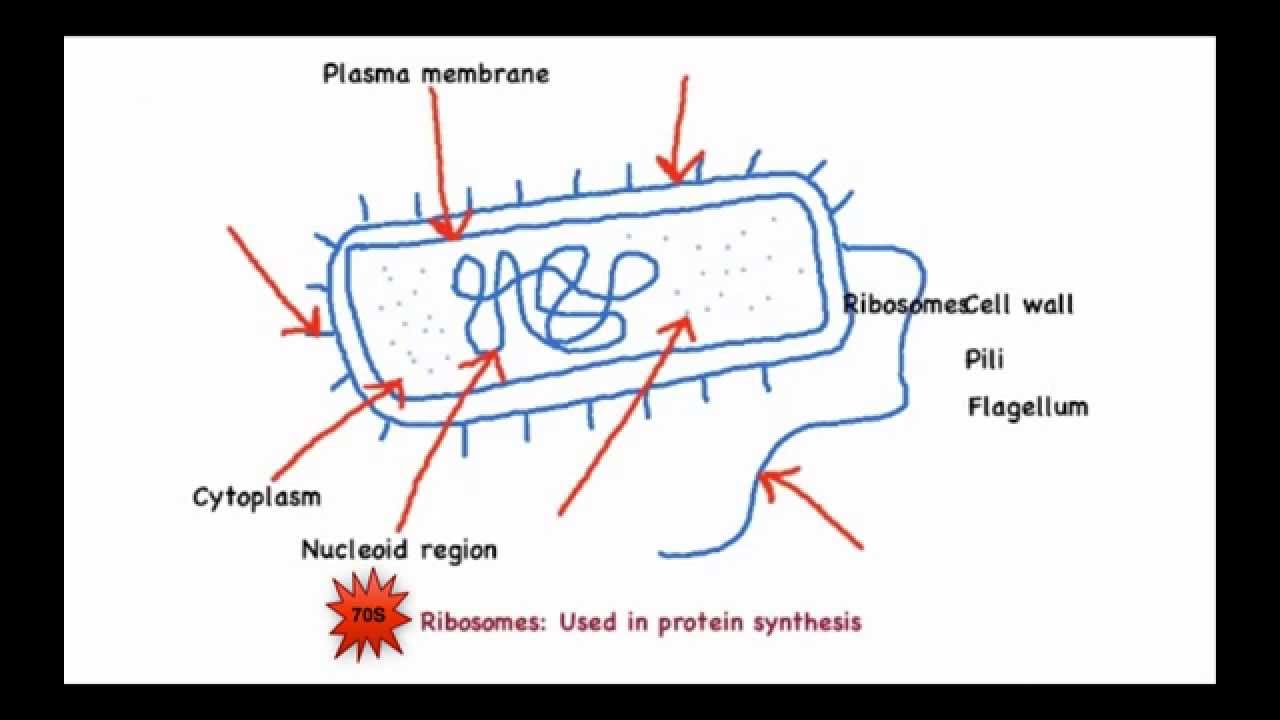
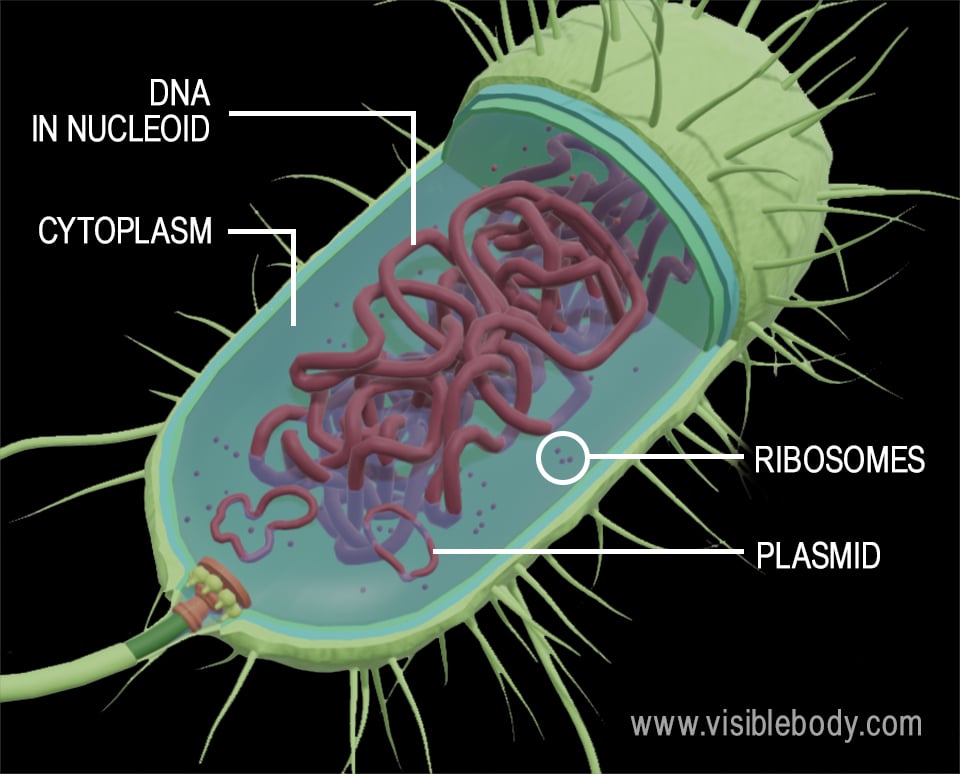
44 label the prokaryotic cell
› bitesize › guidesPlant cells - Cell structure - AQA - GCSE Combined Science ... Plant cells. This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below – the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Protein Synthesis: Definition, Steps, and Diagram - Research … 24.8.2021 · This ribosome is composed of rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and some proteins. It is a cytoplasmic organelle present in both prokaryotic as well as in eukaryotic cells. However, the structure and composition of the ribosome can differ in both the cell. In prokaryotes, the ribosome is composed of 70S subunit whereas eukaryotic organisms consist of 80S ...
alive! Since 1994, CELLS alive! has provided students with a learning resource for cell biology, microbiology, immunology, and microscopy through the use of mobile-friendly interactive animations, video, puzzles, quizzes and study aids.

Label the prokaryotic cell
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell types. Cells are of two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus, but a nucleoid region is still present.. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes may be either single-celled or mult Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model Secretory Vesicle: Cell secretions - e.g. hormones, neurotransmitters - are packaged in secretory vesicles at the Golgi apparatus.The secretory vesicles are then transported to the cell surface for release. Cell Membrane: Every cell is enclosed in a membrane, a double layer of phospholipids (lipid bilayer).The exposed heads of the bilayer are "hydrophilic" (water loving), meaning that … › cell-membrane-373364Cell Membrane Function and Structure - ThoughtCo Oct 07, 2019 · Microscopic view of phospholipids. Stocktrek Images / Getty Images. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes.Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular ...
Label the prokaryotic cell. › animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells - ThoughtCo May 04, 2019 · Animal cells increase in size by increasing in cell numbers. Plant cells mainly increase cell size by becoming larger. They grow by absorbing more water into the central vacuole. Cell Wall . Animal cells do not have a cell wall but have a cell membrane. Plant cells have a cell wall composed of cellulose as well as a cell membrane. Centrioles › books › NBK9940DNA Replication - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf DNA Polymerases. DNA polymerase was first identified in lysates of E.coli by Arthur Kornberg in 1956. The ability of this enzyme to accurately copy a DNA template provided a biochemical basis for the mode of DNA replication that was initially proposed by Watson and Crick, so its isolation represented a landmark discovery in molecular biology. Studying Cells - National Institute of General Medical Sciences … 11.3.2020 · The most prominent organelle is the nucleus, which contains the cell’s genetic material, or DNA (see more on DNA). Prokaryotic cells don’t have a nucleus or other organelles. They are single-celled microorganisms that tend to be smaller than eukaryotic cells. There are two types of prokaryotic cells—bacteria and archaea. Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea, two of the three domains of life.Prokaryotic cells were the first form of life on Earth, characterized by having vital biological processes including cell signaling.They are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and lack a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The DNA of a prokaryotic cell consists of a single circular …
DNA Replication - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf As discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase, which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs) to form the growing DNA chain. However, DNA … en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_biologyCell biology - Wikipedia Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells - ThoughtCo 4.5.2019 · Animal cells and plant cells are similar in that they are both eukaryotic cells.These cells have a true nucleus, which houses DNA and is separated from other cellular structures by a nuclear membrane. Both of these cell types have similar processes for reproduction, which include mitosis and meiosis.Animal and plant cells obtain the energy they need to grow and … Plant cells - Cell structure - AQA - GCSE Combined Science ... - BBC Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances.
Cell Membrane Function and Structure - ThoughtCo 7.10.2019 · Microscopic view of phospholipids. Stocktrek Images / Getty Images. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes.Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from … CELLS alive! Since 1994, CELLS alive! has provided students with a learning resource for cell biology, microbiology, immunology, and microscopy through the use of mobile-friendly interactive animations, video, puzzles, quizzes and study aids. Cell biology - Wikipedia Cell biology (also cellular ... Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, ... Fluorescent markers such as GFP, are used to label a … › cell-membrane-373364Cell Membrane Function and Structure - ThoughtCo Oct 07, 2019 · Microscopic view of phospholipids. Stocktrek Images / Getty Images. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes.Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular ...
Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model Secretory Vesicle: Cell secretions - e.g. hormones, neurotransmitters - are packaged in secretory vesicles at the Golgi apparatus.The secretory vesicles are then transported to the cell surface for release. Cell Membrane: Every cell is enclosed in a membrane, a double layer of phospholipids (lipid bilayer).The exposed heads of the bilayer are "hydrophilic" (water loving), meaning that …
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell types. Cells are of two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus, but a nucleoid region is still present.. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes may be either single-celled or mult














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bacteria_cell_drawing-5786db0a5f9b5831b54f017c.jpg)
Post a Comment for "44 label the prokaryotic cell"