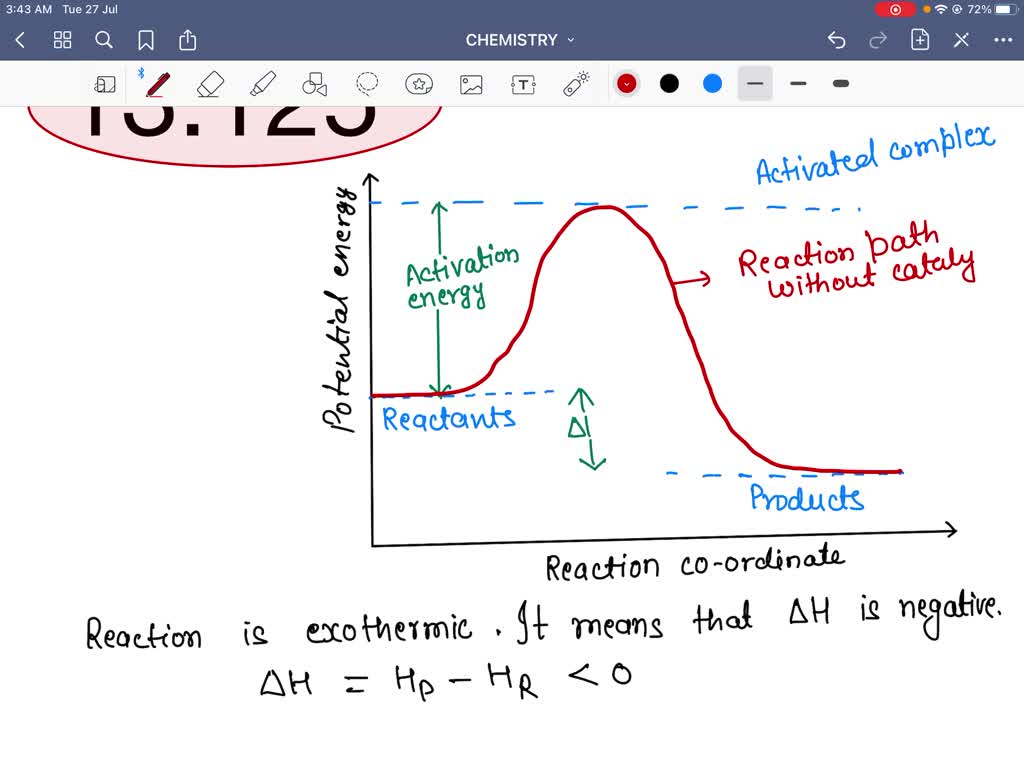
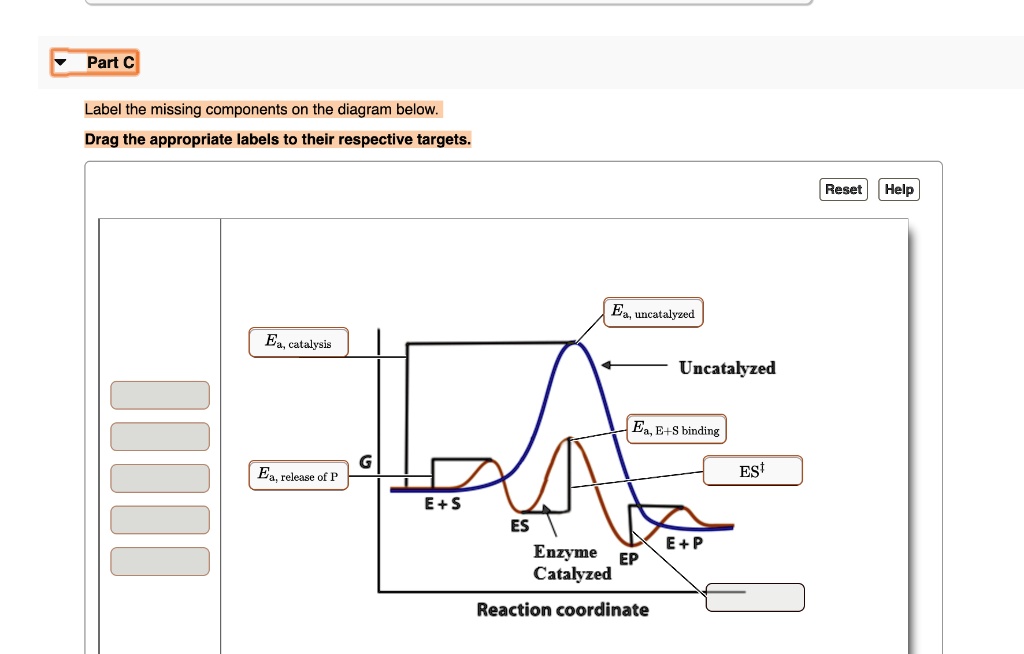
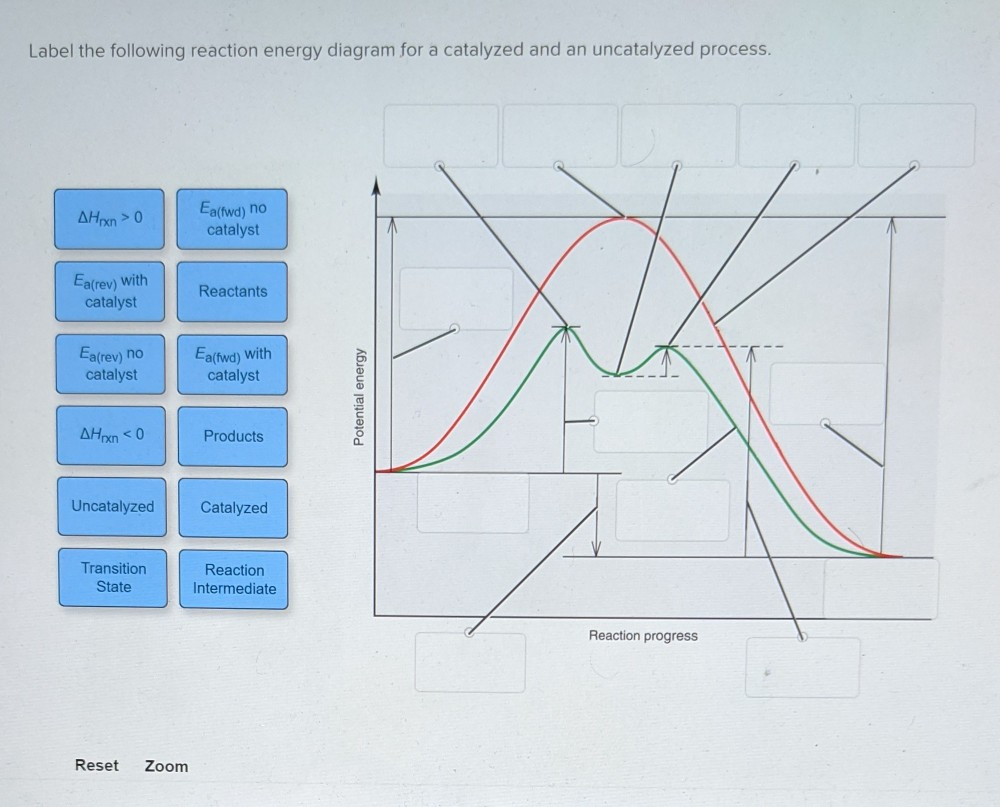
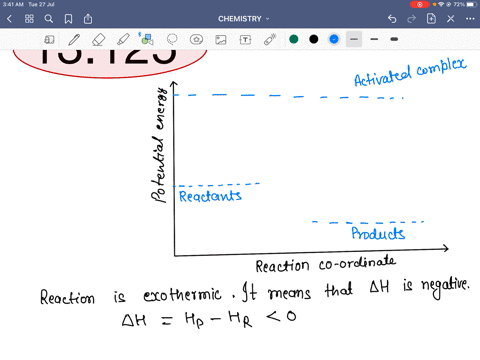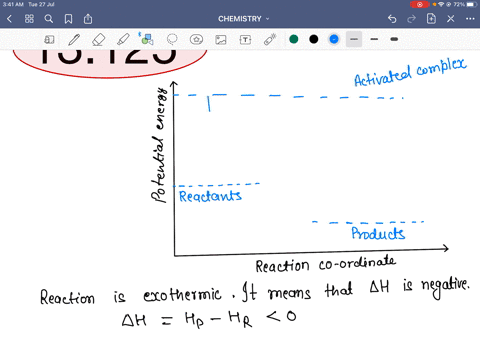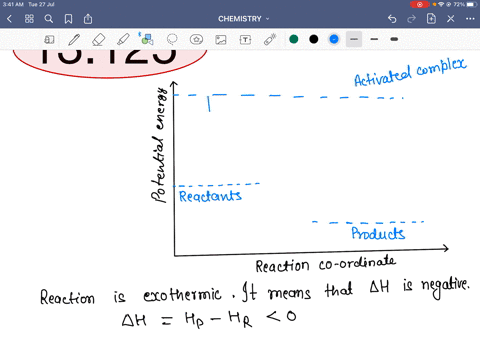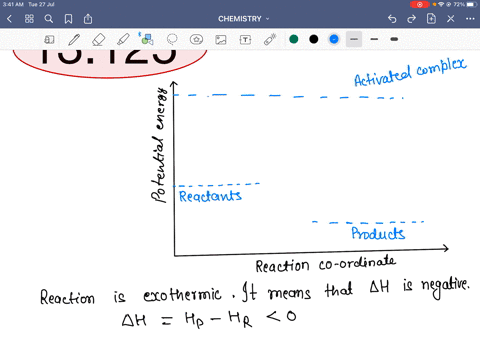
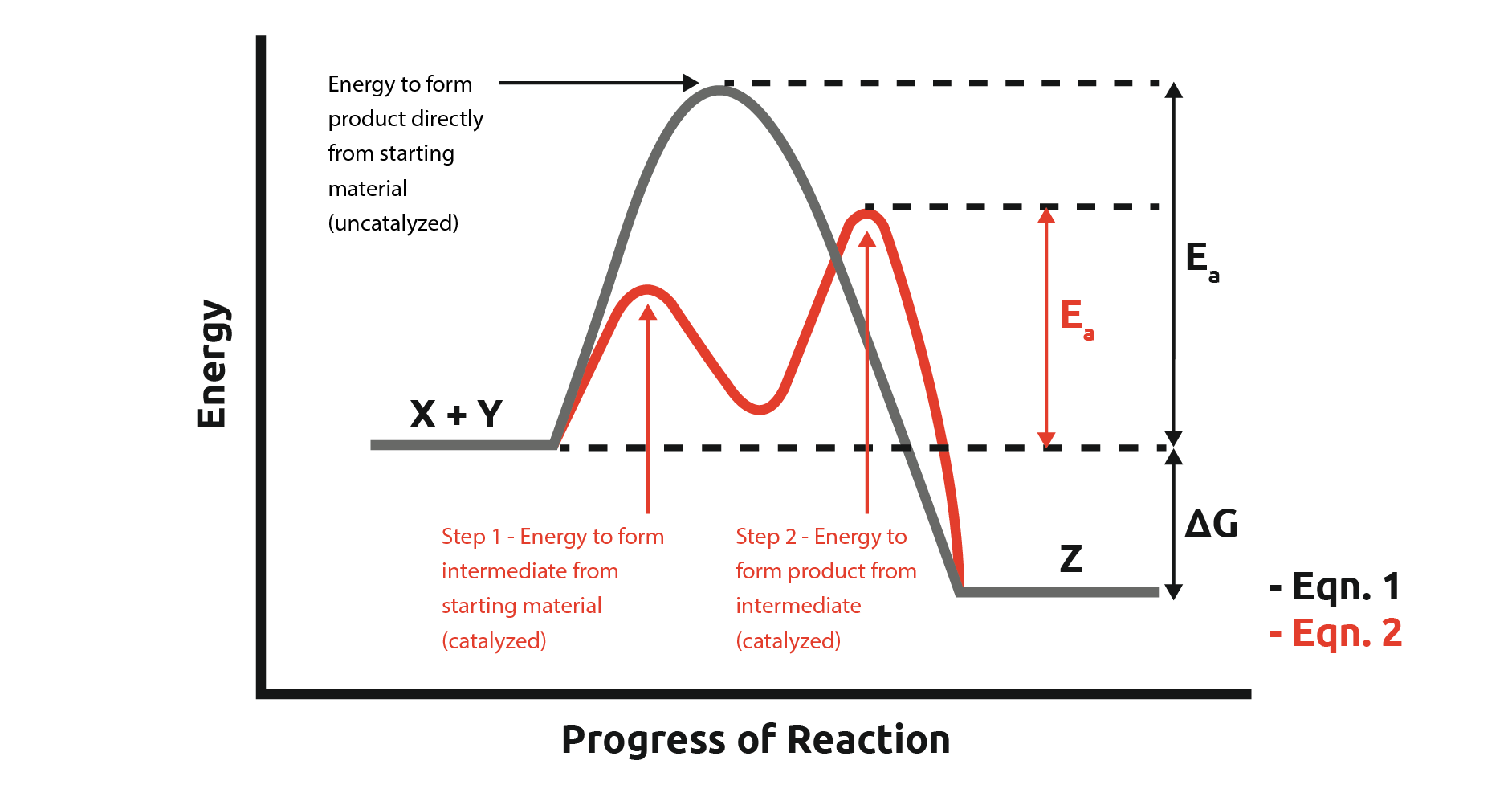
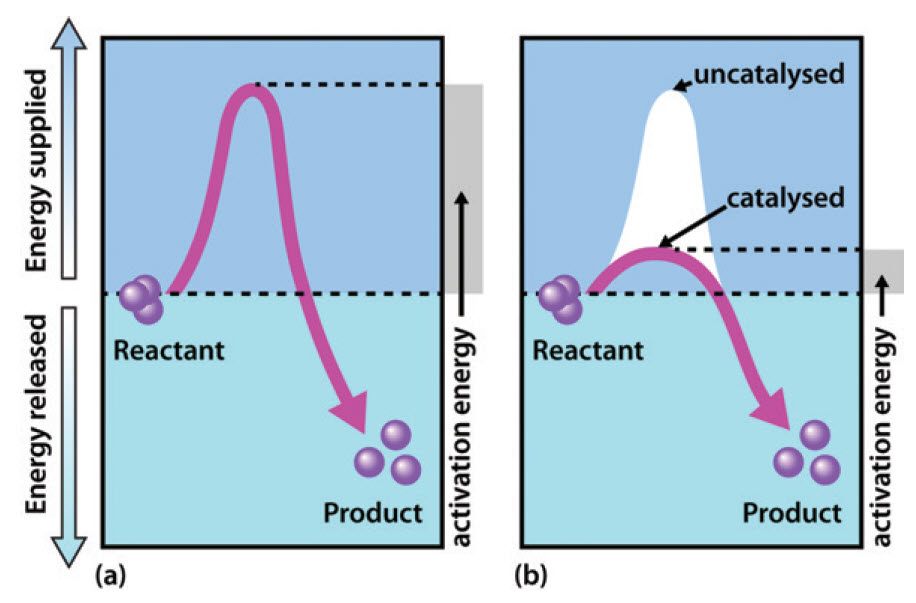
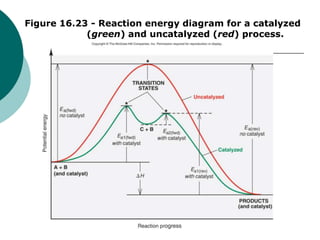
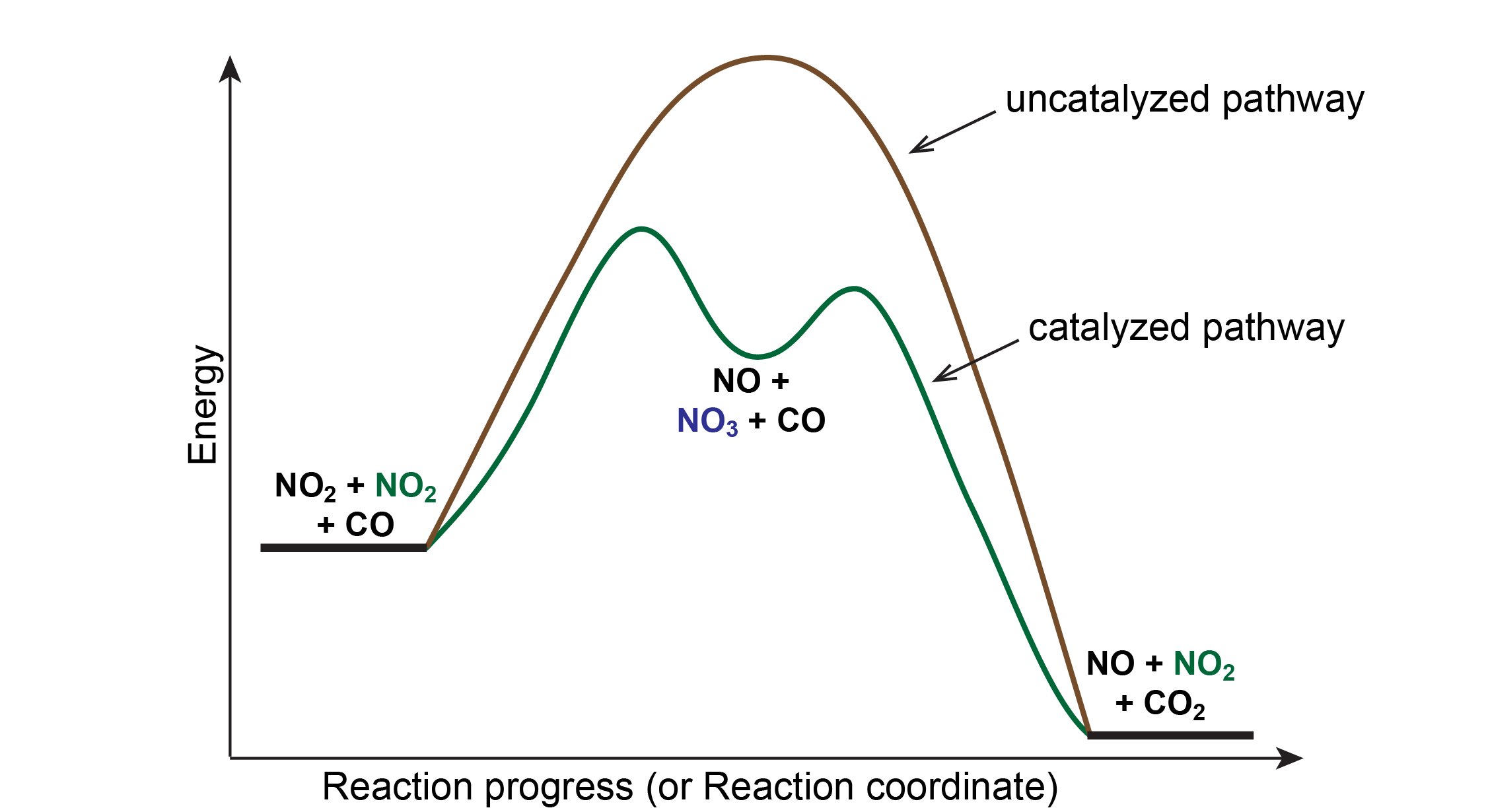
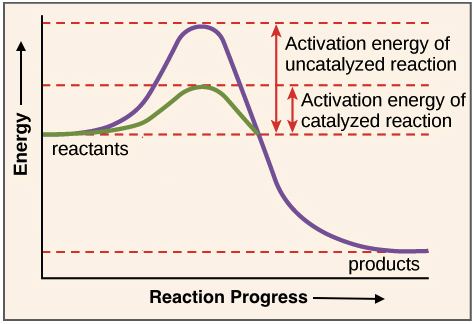
45 reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
dokumen.pub › biochemistry-9th-editionBiochemistry [9th edition.] 9781305961135, 1305961137 ... A reaction that takes place as a part of many biochemical processes is the hydrolysis of the compound ATP, as shown in Figure 1.29 (Section 1-2). This reaction releases energy (30.5 kJ mol 21 ATP 5 7.3 kcal/mol ATP). More to the point, the energy released by this reaction allows energy-requiring reactions to proceed. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Transition_state_theoryTransition state theory - Wikipedia In 1931, Henry Eyring and Michael Polanyi constructed a potential energy surface for the reaction below. This surface is a three-dimensional diagram based on quantum-mechanical principles as well as experimental data on vibrational frequencies and energies of dissociation. H + H 2 → H 2 + H
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Enzyme_catalysisEnzyme catalysis - Wikipedia 1) S 2 + EP 2 → S 2 EP 2 → P 2 + EX 2 (2) It may be seen from reaction (1) that the group X 1 of the active enzyme appears in the product due to possibility of the exchange reaction inside enzyme to avoid both electrostatic inhibition and repulsion of atoms. So we represent the active enzyme as a powerful reactant of the enzymatic reaction. The reaction (2) shows incomplete conversion of ...
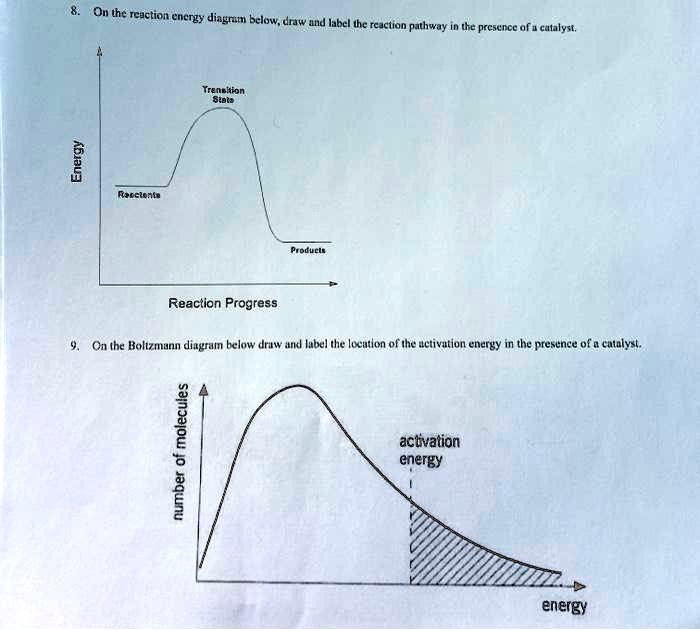
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
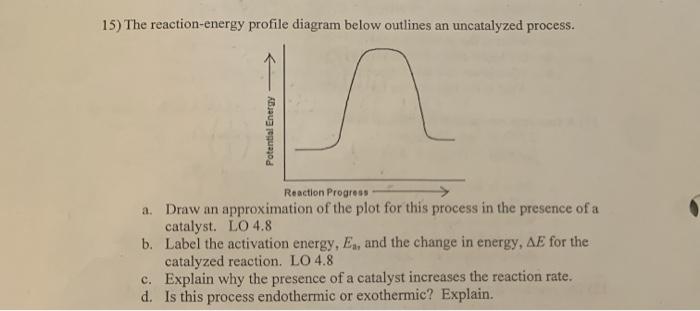
› 80127975 › Bioprocess_Engineering(PDF) Bioprocess Engineering-Basic Concepts by Shuler and ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. wou.edu › chemistry › coursesCH103 – Chapter 7: Chemical Reactions in Biological Systems ... Figure 7.15 Gibbs Free Energy Diagram of an Enzyme Mediated Reaction. The reaction energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is shown in red. Note that the transition state of the reaction is the most unstable part of the reaction and thus, is the position on the graph with the highest free energy. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EnzymeEnzyme - Wikipedia 1) CO 2 + H 2 O ← Carbonic anhydrase H 2 CO 3 {\displaystyle {\ce {CO2{}+H2O<-[{\text{Carbonic anhydrase}}]H2CO3}}} (in lungs ; low CO 2 concentration) (2) The rate of a reaction is dependent on the activation energy needed to form the transition state which then decays into products. Enzymes increase reaction rates by lowering the energy of the transition state. First, binding forms a low ...
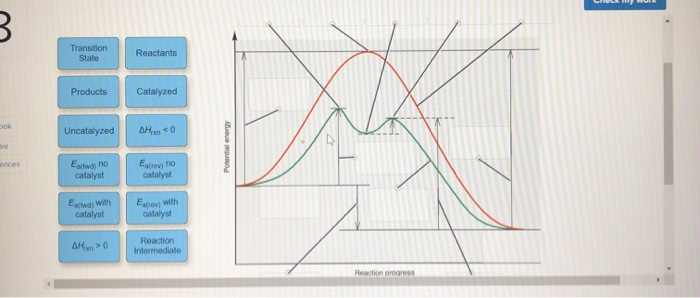
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. quizlet.com › 652206399 › ap-bio-s1-final-part-1AP Bio S1 Final Part 1 Flashcards | Quizlet The diagram below compares the reaction coordinates for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed pathways of this reaction. Which of the following statements about letter C is true? Letter C represents the activation energy of the uncatalyzed reaction pathway. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EnzymeEnzyme - Wikipedia 1) CO 2 + H 2 O ← Carbonic anhydrase H 2 CO 3 {\displaystyle {\ce {CO2{}+H2O<-[{\text{Carbonic anhydrase}}]H2CO3}}} (in lungs ; low CO 2 concentration) (2) The rate of a reaction is dependent on the activation energy needed to form the transition state which then decays into products. Enzymes increase reaction rates by lowering the energy of the transition state. First, binding forms a low ... wou.edu › chemistry › coursesCH103 – Chapter 7: Chemical Reactions in Biological Systems ... Figure 7.15 Gibbs Free Energy Diagram of an Enzyme Mediated Reaction. The reaction energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is shown in red. Note that the transition state of the reaction is the most unstable part of the reaction and thus, is the position on the graph with the highest free energy. › 80127975 › Bioprocess_Engineering(PDF) Bioprocess Engineering-Basic Concepts by Shuler and ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
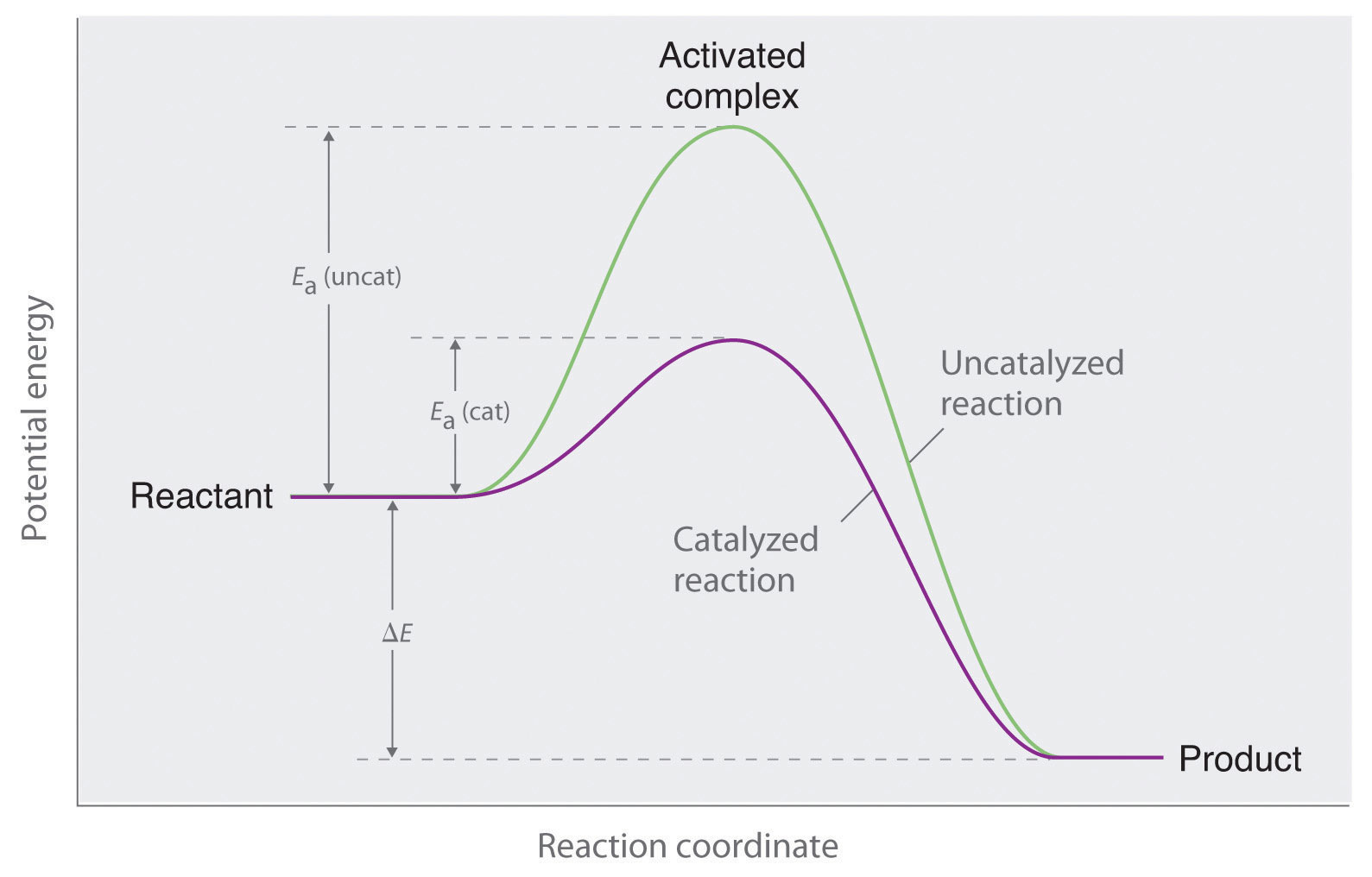




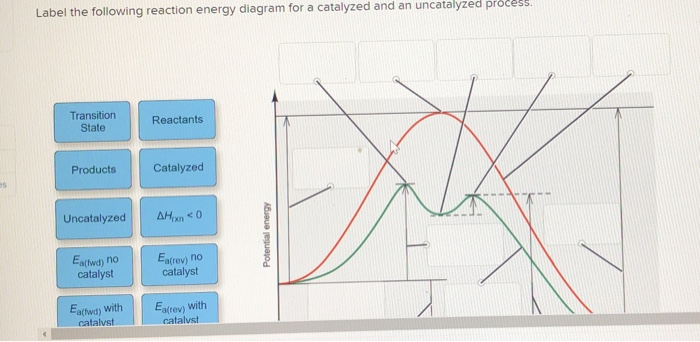















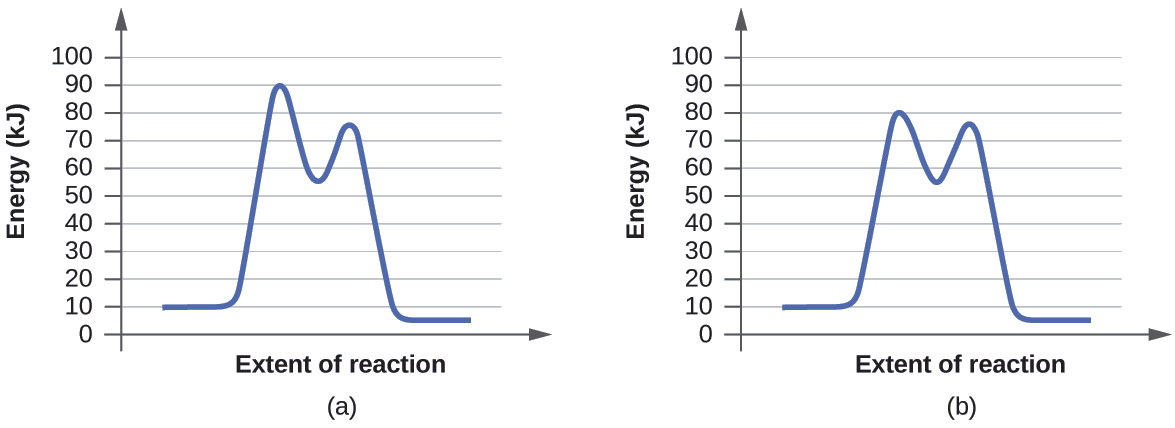

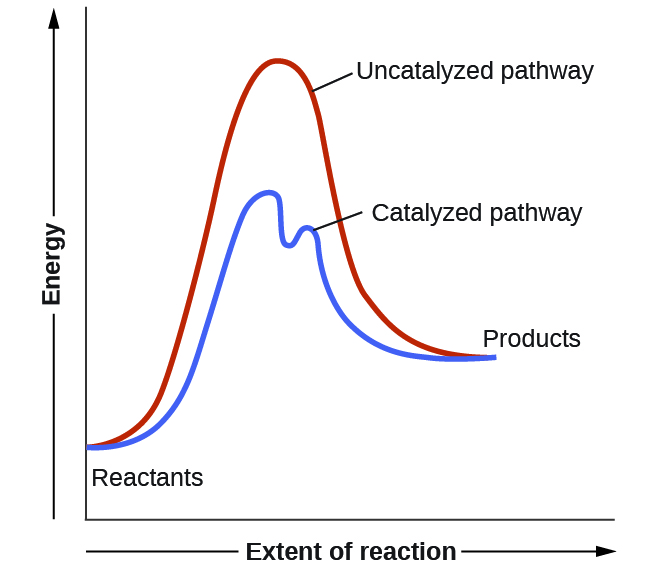
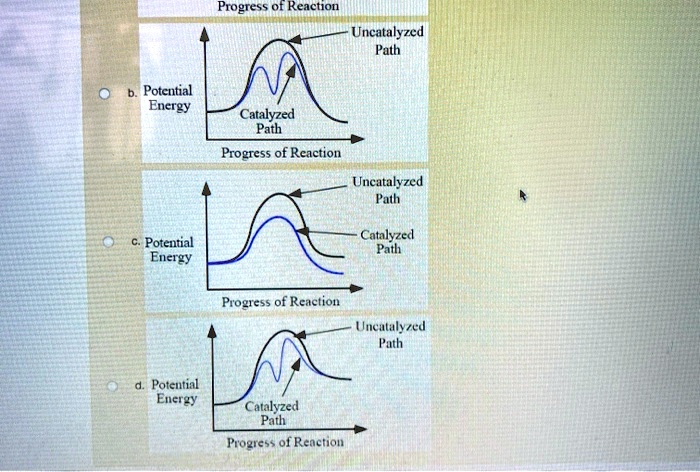


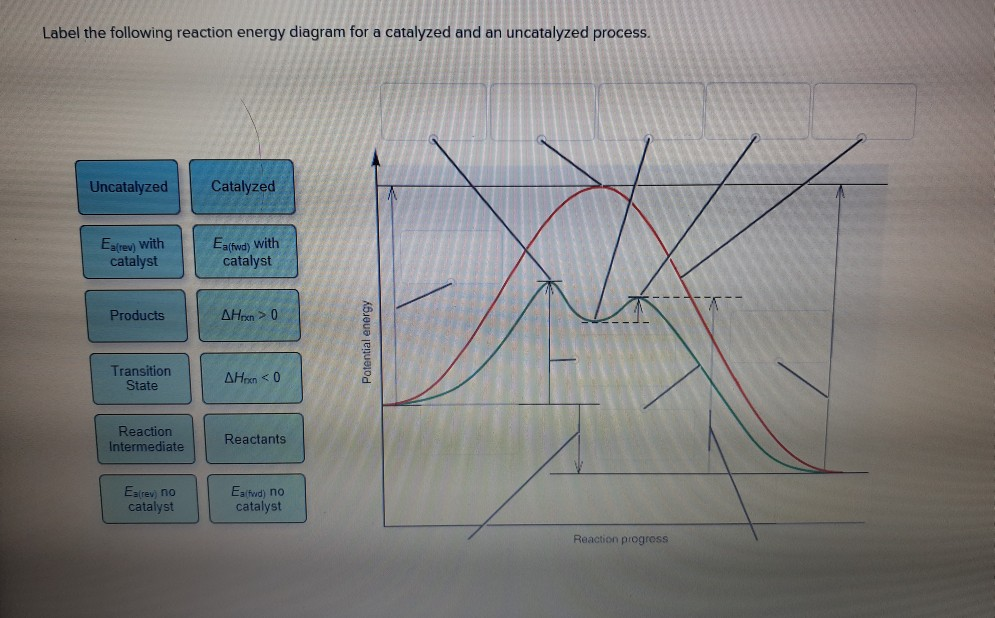


Post a Comment for "45 reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process"